Drilling oil and gas wells isn’t just about punching a hole into the earth. It’s a complex symphony of mechanical systems, each playing its part to ensure precision, safety, and efficiency. In this blog, we break down the four primary drilling rig systems—Power, Hoisting, Rotating, and Circulating—and explain how they work together on a rig site.
This is your next step after understanding drilling rig components—now, let’s see them in action.
Table of Contents
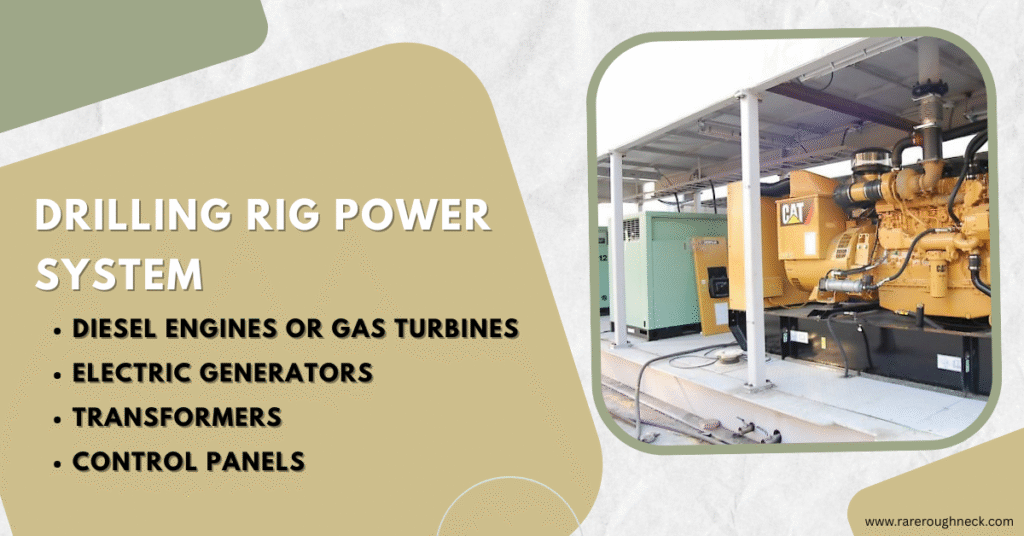
1. Power System – The Energy Core of the Rig
Every drilling rig begins with power. It’s the backbone of the entire operation, supplying energy to all other systems.
What It Includes:
- Diesel engines or gas turbines
- Electric generators
- Control panels and transformers
How It Works:
Engines drive generators, converting mechanical energy into electricity that powers the drawworks, rotary system, pumps, lights, and safety systems.
Real-Life Example:
In the Permian Basin, land rigs often use dual-fuel generators that run on both diesel and natural gas, reducing operational costs and emissions. These systems power everything from mud pumps to the camp’s air conditioning.
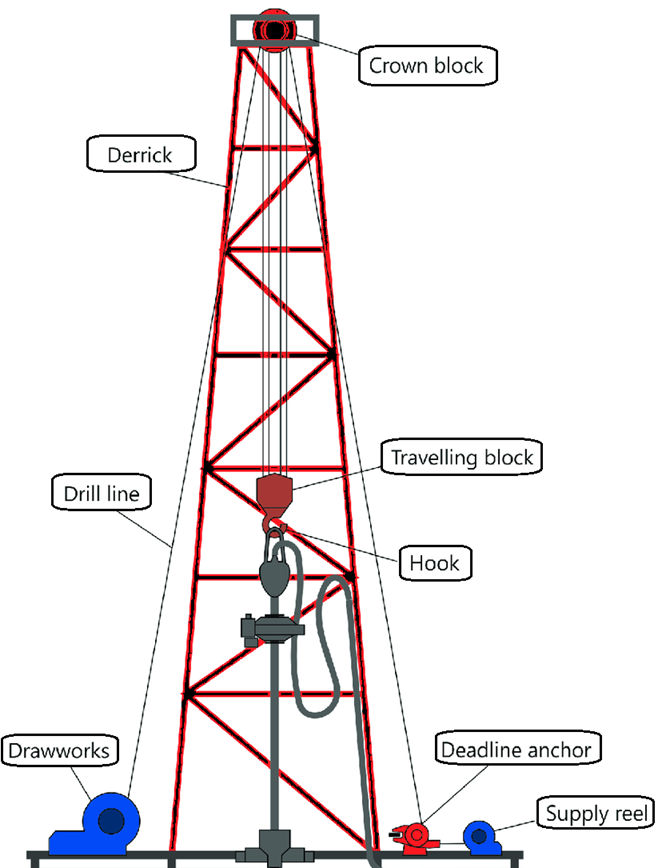
2. Hoisting System – The Rig’s Heavy Lifter
The hoisting system is what lifts and lowers the heavy drill string into the well. It’s made up of cables, pulleys, and winches that support thousands of pounds of equipment.
Key Components:
- Drawworks
- Crown block & traveling block
- Drilling line
- Hook and elevators
Real-Life Analogy:
Think of it like a crane on steroids—except it’s vertical, precise, and operates 24/7 in all conditions. One common operation is tripping pipe, where 30–40-ton strings are pulled out to change the drill bit or casing.
Example in Action:
In offshore rigs like Transocean’s Deepwater Asgard, automated drawworks systems hoist pipe vertically with pinpoint control, helping reduce crew fatigue and avoid accidents.
3. Rotating System – The Earth Mover
This is what gives the drill bit its rotational force to grind through rock. Without it, drilling wouldn’t happen.
Main Components:
- Rotary table (old school) or Top Drive (modern)
- Kelly or drill pipe
- Swivel
Real-Life Shift:
Most modern rigs now use top drive systems, which are safer and more efficient. Top drives spin the drill string from above and allow the use of longer stands of pipe, reducing connection time.
Field Insight:
In the Middle East, moving from rotary tables to top drives on rigs reduced non-productive time (NPT) by over 15%, saving operators millions in downtime costs.
4. Circulating System – The Bloodstream of the Well
The circulating system pumps drilling fluid (mud) down the hole and back up. It cools the bit, removes rock cuttings, and balances formation pressure.
Includes:
Real-Life Example:
In the North Sea, high-pressure pumps circulate synthetic-based muds at over 5,000 psi. This ensures stable boreholes and efficient cuttings removal in tough offshore conditions.
Bonus: Well Control System – The Rig’s Emergency Brake
Though not one of the primary four, well control systems like Blowout Preventers (BOPs) are absolutely critical. They prevent uncontrolled pressure surges (kicks) from causing blowouts.
Used During:
- Unexpected gas surges
- High-pressure formations
- Well testing and completion
How It All Works Together: A Day on the Rig
Let’s imagine a real scenario:
- The power system energizes the site at 6 a.m.
- Crew hoists a 30-meter drill pipe stand into position.
- The top drive begins rotating as pumps circulate mud.
- After 3 hours, the mud weight changes, indicating a possible formation shift.
- The BOP is tested, and drilling resumes after pressure balance is confirmed.
Each system must perform flawlessly, or drilling halts—costing thousands per hour.
Drilling rig systems are more than mechanical assemblies—they’re the nerve center of modern energy exploration. Understanding how they work together helps rig crews, engineers, and even energy investors appreciate what goes into every barrel of oil produced.
If you enjoyed this, check out our next deep dive into Automation in Drilling Rigs, where we explore how AI and robotics are shaping tomorrow’s oilfield.


Pingback: Global Offshore Oil & Gas Highlights – July 2025 Edition - rareroughneck.com