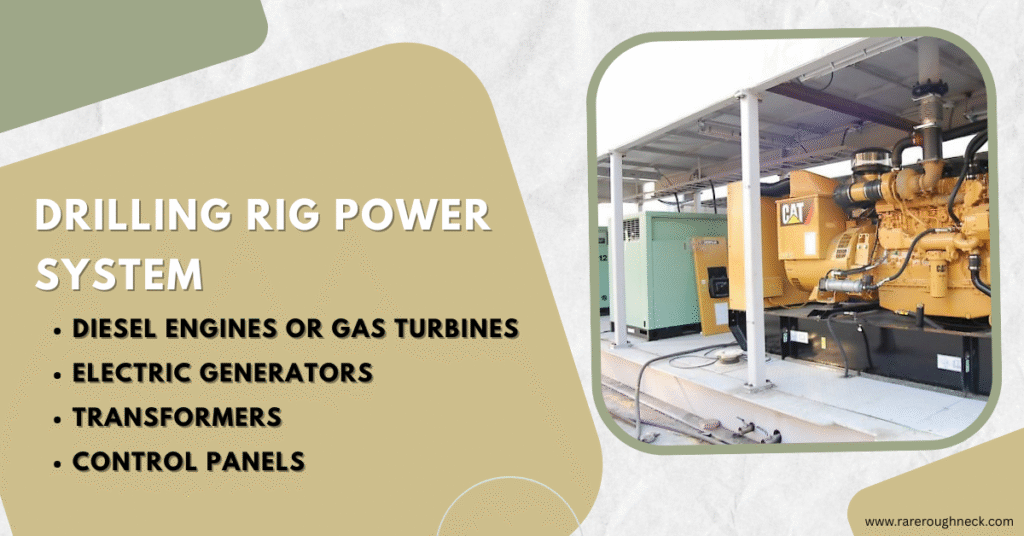
The Drilling Rig Power System is the core energy source that powers every function on a drilling rig—whether it’s hoisting heavy drill pipes, rotating the drill bit, or circulating drilling mud. Without a reliable power system, drilling operations come to a halt.
In this blog, we’ll break down the components of the drilling rig power system, explain how each part works, and offer real-world examples that even non-engineers can understand.
Key Components of a Drilling Rig Power System
The power system on a drilling rig converts fuel into electrical energy and distributes it to vital systems like top drives, drawworks, and mud pumps.
1. Diesel Engines or Gas Turbines – The Heart of the Rig
The first stage of a drilling rig power system begins with converting fuel into mechanical energy using:
- Diesel Engines: The most widely used power source on land rigs due to their ruggedness and ease of maintenance.
- Example: The Caterpillar 3512C delivers 1500+ horsepower and is a top choice for land-based rigs worldwide.
- Gas Turbines: Preferred for high-capacity offshore rigs where reduced emissions and compact size matter.
- Example: GE’s LM2500 gas turbine, offering 30,000+ HP, is often seen on drillships and semi-submersibles.
2. Electric Generators – Turning Motion into Electricity
Once mechanical energy is generated, it powers electric generators, which convert it into electrical power.
- These generators supply energy to systems like:
- Top drive (for rotation)
- Drawworks (for hoisting)
- Mud pumps (for circulation)
- Lighting and auxiliary units
- Real-World Brand: ABB and Siemens manufacture durable and efficient rig generators for harsh environments.
3. Transformers – Adjusting Voltage Levels
ransformers manage the voltage output from generators:
- Step-down transformers are used for low-voltage needs like lighting and control units.
- Step-up transformers power high-voltage systems like top drives.
This component ensures smooth and safe power distribution throughout the rig.
4. Control Panels – The Central Command Unit
Control panels act as the brain of the drilling rig power system, monitoring and managing the flow of electricity.
- Operators can adjust engine speed, track generator loads, and troubleshoot power issues in real-time.
- Modern panels come with digital displays and alarms for enhanced safety.
Real-Life Example: Power System on a Texas Land Rig
Imagine a land rig in Permian Basin, West Texas:
- It uses three Caterpillar diesel engines, each connected to 1000 kW generators.
- Power is routed through transformers to motor control centers (MCCs).
- Electricity runs:
- The top drive
- Triplex mud pumps
- Lighting, HVAC, and control systems
How the Drilling Rig Power System Works – Simplified
Think of the system as a human body:
- Engines = Heart (generate energy)
- Generators = Lungs (convert energy)
- Transformers = Arteries (regulate energy flow)
- Control Panels = Brain (distribute energy wisely)
If one fails, the rig can’t function safely or efficiently.
Backup and Safety Systems
Emergency Shutdown (ESD): Cuts off power in case of fire, gas leaks, or blowouts.
Backup Generators: Kick in during power failure to prevent costly downtime.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Keep critical controls and communication online during outages.