Every drilling rig relies on one system that literally keeps the wellbore advancing – the Rotating System in Drilling Rig.
Its job is simple but vital: to make the drill bit spin and grind through layers of rock thousands of feet below the surface.
If the Power System is the rig’s engine and the Hoisting System is its muscle, the Rotating System is the motion that brings everything to life.
In this post, we’ll explore each major component – Rotary Table, Kelly, Swivel, and Top Drive – with easy explanations, examples, and real-world insights.
What Does the Rotating System Do?
The Rotating System in Drilling Rig transmits torque from the rig’s power source to the drill string and finally to the drill bit at the bottom of the well.
This torque lets the bit cut, crush, and grind rock formations while drilling mud circulates to cool and clean the hole.
Energy flows from:
Engines → Generators → Rotary Table or Top Drive → Kelly → Drill Pipe → Drill Bit
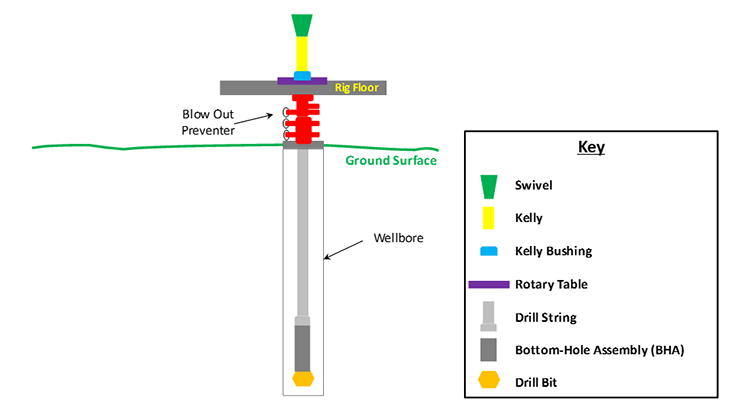
1. Rotary Table – The Classic Rotating Platform
Before modern automation, rigs used a rotary table – a heavy, circular steel turntable set into the drill floor.
Main Components
- Rotary table base – mounted on bearings, driven by chains or electric motors.
- Master bushing – fits inside the table and supports the kelly bushing.
- Kelly bushing – grips the kelly and transmits torque to it.
- Rotary lock – secures the table when tripping pipe or connecting stands.
When the rotary table spins, torque travels through the kelly into the drill string.
Example
Older land rigs in Gujarat or Rajasthan still use rotary tables for shallow exploration wells (< 3 000 m).
They’re simple, rugged, and require minimal electronics – making them ideal for remote onshore operations.
Advantages
- Reliable mechanical drive
- Lower cost & easy maintenance
Limitations
- Manual pipe handling (slower)
- Harder to control torque precisely
- Not suited for complex directional wells
2. Kelly & Kelly Drive – Connecting Surface Power to the String
The kelly is a square or hexagonal steel pipe that fits into the rotary table’s kelly bushing.
It’s the link that transmits rotation from the surface to the drill pipe.
How It Works
As the rotary table turns, the kelly’s shape locks into the bushing, forcing it (and the drill string below) to rotate.
At the same time, drilling mud flows through the hollow center of the kelly into the drill pipe.
Key Parts
- Kelly cock valves – prevent blowouts when disconnected.
- Saver sub – protects the threaded connection between kelly and drill pipe.
- Drive bushing – fits into the master bushing of the rotary table.
Think of the rotary table as a car’s engine and the kelly as the drive shaft that delivers torque to the wheels.
Example
A 4 ¾-inch hexagonal kelly can easily handle torques of 30 000 ft-lb, transmitting power to a 10 000-ft drill string.
3. Swivel – Letting It Spin and Flow
The swivel sits at the top of the drill string, connecting it to the hoisting system via the hook.
It has two critical jobs:
- Supports the entire weight of the drill string.
- Allows drilling mud to flow down through the kelly while letting the string rotate freely.
Main Components
- Bail – connects to the traveling block hook.
- Gooseneck – the high-pressure inlet for drilling mud.
- Washpipe & packing – prevent leaks while rotating.
- Bearing assembly – lets the string spin smoothly under load.
Example
When mud pumps push fluid at 3 000 psi, the swivel’s washpipe seals maintain pressure while rotation continues at ~120 RPM – without a single drop leaking.
4. Top Drive System – The Modern Rotating Technology
The Top Drive replaced the rotary table and kelly in most modern rigs.
It’s a motorized unit mounted on rails in the derrick that directly rotates the drill string.
Key Parts
- Electric or hydraulic motor – provides rotation and torque.
- Gear box and quill – transfer torque to the drill string.
- Torque track system – prevents twisting in the derrick.
- Saver sub & elevator link – connects to the top of the drill pipe.
How It Works
The top drive moves up and down with the traveling block, allowing drilling with longer stands (2 or 3 joints) before stopping to make a connection – saving time and improving safety.
Example
A NOV TDS-11 SA top drive, powered by a 1 150 HP motor, can deliver up to 80 000 ft-lb torque – enough to drill 25 000-ft deep offshore wells continuously.
Advantages
- Faster connection time (≈ 2 minutes → 1 minute)
- Safer: fewer floor operations
- Ideal for directional & extended-reach drilling
Limitations
- Higher initial cost
- Requires electrical/hydraulic maintenance
Rotary Table vs Top Drive – Quick Comparison
| Feature | Rotary Table + Kelly | Top Drive System |
| Torque Transmission | Indirect (via kelly drive) | Direct motor to drill string |
| Connection Speed | Slow (manual) | Fast (automatic) |
| Directional Drilling | Difficult | Highly accurate |
| Safety | Manual pipe handling | Automated control |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Higher |
| Common Use | Land / conventional rigs | Modern land & offshore rigs |
Real-World Example – Rig Upgrade in Oman
A drilling contractor in Oman upgraded an old 1 500 HP land rig from a rotary table + kelly setup to a top drive.
After the upgrade:
- Connection time dropped from 3 min → 1 min per stand.
- Average drilling speed increased by 18 %.
- Manual handling injuries fell significantly.
This single change added ~1 000 ft/day of drilling progress – a clear ROI in just months.
Also Check : Hoisting System in Drilling Rig
Safety & Maintenance Checklist
- Swivel seals & washpipe: inspect weekly for leaks.
- Kelly bushing: check for wear or cracks.
- Rotary table chains & bearings: grease daily.
- Top drive gear oil & filters: monitor pressure & temperature.
- Torque monitoring system: calibrate monthly.
Keeping the rotating system in top shape means fewer breakdowns and smoother drilling.
Key Takeaways
- The Rotating System in Drilling Rig converts power into rotational force to cut through rock.
- It includes rotary table, kelly, swivel, and the modern top drive.
- Top drives have revolutionized drilling with speed, safety, and precision.
- Proper inspection and maintenance keep the rotation smooth and safe.
Conclusion
From the rhythmic hum of a rotary table to the precision of a top drive, the rotating system has evolved dramatically.
It’s what turns horsepower into hole progress – literally powering every meter drilled.
As rigs become smarter and automation expands, the rotating system will remain the heart of the drilling process, continuously refined for efficiency and safety.


Pingback: Rotary Table in Drilling Rig – Components, Working, Maintenance & Safety